The Microalgae Spirulina
Use
- Food for young fish
- Supplementary food for fish and decapods
- Own food mixtures
Systematics
- Phylum Cyanophyta (blue-green algae/cyanobacteria)
- Family Cyanophyceae
- Genus Spirulina (corkscrew algae)
- Species platensis (large c.), abbreviata (small c.), jenneri (blue-green c.)
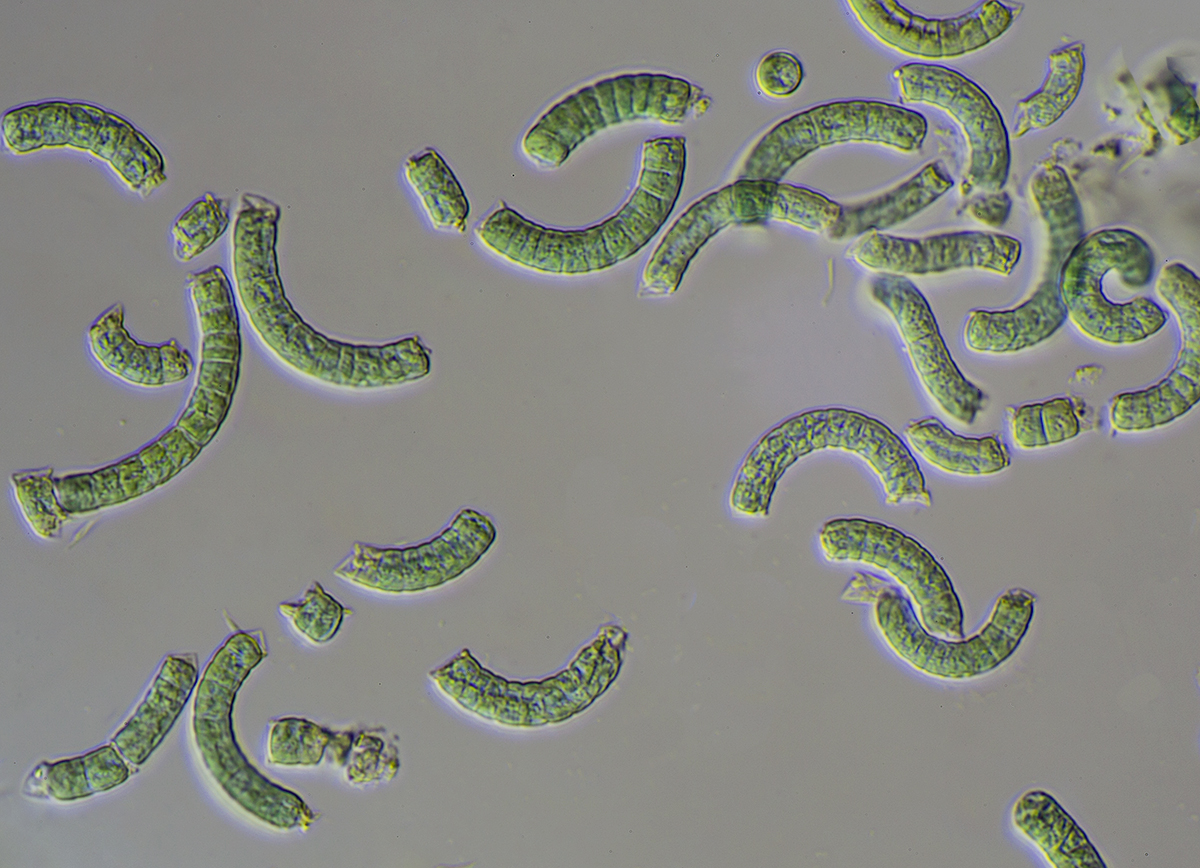
- Large corkscrew algae - originally native to the soda lakes of the (sub)tropics (not marine algae)
- Filaments helically wound, slightly constricted at the transverse walls, planktonic or in layers
- Cells square or shorter than wide
- Cells 2 - 6 µm long, 6 - 8 µm wide, coils of filaments 25 - 40 µm wide, circumferences 45 - 60 µm apart
- In stagnant waters, where it can cause huge aquatic blooms
Culture
Today it is cultivated worldwide in the appropriate climate zones in a strongly alkaline medium (13.61 g NaHCO3 / 4.03 g Na2CO3 per litre of water [pH 9]).
Fertilise with nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus (phosphate), sulphur (sulphate), magnesium and trace elements (calcium, iron, zinc, manganese, boron, cobalt, molybdenum and copper).
The culture must be aerated.
The extraction is carried out gently by spray drying; on a laboratory scale also gently by pouring over gauze.
Literature
Dr Ingo Botho Reize, DATZ 54(2), 60 (2001). - Brief report
Dr Ingo Botho Reize, Koralle 2(8), 36 (2001).
Typical composition
| General | [%] |
| Protein | 60.4 |
| Carbohydrates | 12.6 |
| Fats | 4.9 |
| Moisture | 5.6 |
| Ash | 8.0 |
| Crude fibre | 8.5 |
| Protein | [%] |
|
Amino acids, essential |
|
| Isoleucine | 4.8 |
| leucine | 7.1 |
| Lysine | 7.5 |
| Methionine | 2.0 |
| Phenylalanine | 3.6 |
| Threonine | 8.3 |
| Tryptophan | 2.4 |
| Valine | 5.1 |
|
Amino acids, non-essential |
|
| Alanine | 5.4 |
| Arginine | 5.2 |
| Aspartic acid | 6.0 |
| Cystine | 0.6 |
| Glutamic acid | 8.6 |
| Glycine | 6.6 |
| Histidine | 1.0 |
| Proline | 5.6 |
| Serine | 3.6 |
| Tyrosine | 2.5 |
| Carbohydrates | [%] |
| Ramnose | 9.0 |
| Glucan | 1.5 |
| Phosphorilated cyclitols | 2.5 |
| Glucosamine + Muramic acid | 2.0 |
| Glycogen | 0.5 |
| Fats (fatty acids) | [mg/kg] |
| Lauric acid (C12) | 229 |
| Myristic acid (C14) | 582 |
| Palmitoleic acid (C16) | 1.762 |
| Palmitic acid (C16) | 18.820 |
| Palmitoleic acid (C16) | 2.157 |
| Heptadecanoic acid (C17) | 116 |
| Oleic acid (C18) | 2.489 |
| Total Linoleic acid (C18), of which | 12.350 |
| γ-Linolenic acid (C18) | 11.900 |
| α-Linolenic acid (C18) | 293 |
| Colouring agents | [mg/kg] |
| Carotenoids, total | 3.350 |
| of which β-Carotene | 1.200 - 1.800 |
| Chlorophyll | 11.800 |
| Phycocyanin | 12.000 - 15.000 |
| Nucleic acids | [%] |
| RNA - Ribonucleic acid | 2.8 |
| DNA - Deoxyribonucleic acid | 0.8 |
| Vitamins | [mg/kg] |
| Biotin (H) | 0.4 |
| Cyanocobalamin (B12) | 0.11 |
| Ca-Pantothenate | 11.0 |
| Folic acid | 0.5 |
| Inositol | 350 |
| Niacin | 118 |
| Pyridoxine (B6) | 6.0 |
| Riboflavin (B2) | 40.0 |
| Thiamine (B1) | 55.0 |
| Tocopherol (E) | 10 - 60 |
| Ubiquinone (Q10) | 2.0 |
| Minerals / trace elements | [mg/kg] |
| Calcium (Ca) | 3.200 |
| Phosphorus (P) | 6.800 |
| Iron (Fe) | 360 |
| Sodium (Na) | 3.310 |
| Chloride (Cl) | 144 |
| Magnesium (Mg) | 4.350 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 48 |
| Zinc (Zn) | 50 |
| Potassium (K) | 1.530 |
| Selenium (Se) | 0.5 |
| Lithium (Li) | 0.35 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 3.2 |
| Copper (Cu) | 3.0 |
| Iodine (I) | 12.6 |
| Enzymes | [Units/g] |
| SOD (superoxide dismutase) | 242 |
| Glutathione peroxidase | 3.32 |
| Heavy metals | [mg/kg] |
| Arsenic (As) | < 0.10 |
| Lead (Pb) | < 0.07 |
| Cadmium (Cd) | < 0.10 |
| Mercury (Hg) | < 0.01 |

