Physics
Density
With a density of 1.977 kg/m3 under standard conditions (1013 mbar, 0 °C), CO2 is around 1.5 times heavier than air and can therefore displace it in deeper areas when it escapes. There is therefore a risk of suffocation from the colourless and odourless gas.
Dissociation
Carbon dioxide is a very stable compound. Dissociation into carbon monoxide and oxygen only begins slowly at 1,700 °C. At this point, the equilibrium is still 98 %. At this point, 98 % of the equilibrium is still in favour of CO2.
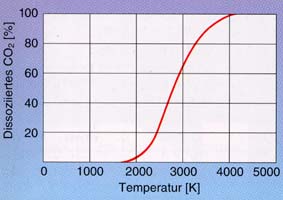 |
CO2 |
States of aggregation
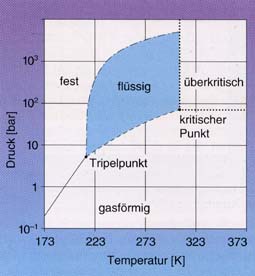 |
Phase diagram (T, p) of CO2 |
Solid
The commercial name for solid carbon dioxide is dry ice. The name comes from the fact that it sublimates directly at ~ -79 °C without a transition to the liquid phase.

