Anthelmintics
Warning
The active ingredients described below are contained in prescription-only preparations. These can often be obtained directly from the vet. Otherwise, very large minimum quantities usually have to be ordered. If you ask the pharmacist to dispense the preparations to you in this way, bypassing the vet, you make yourself and the pharmacist liable to prosecution under the Medicines Act; you should be aware of this risk. This also applies to the supply of such preparations in a club or from other aquarists.
Levamisole
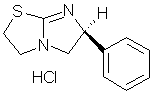
IUPAC: L(-)-2,3,5,6-tetrahydro-6-phenylimidazo-[2,1-B]thiazole hydrochloride
Molecular formula: C11H12N2S× HCl (MW: 204.29 × 36.46)
Application and effect
Levamisole paralyses the muscles of the worms.
A solution of 300 - 600 mg/l levamisole hydrochloride is used. Live red mosquito larvae (or other feed) are treated in this solution for 0.5 - 1 hour and then fed to the infested fish.
A less gentle method, but also effective for fish that no longer eat, is bath treatment:
Dosage: 5 - 7 mg/l levamisole hydrochloride
After treatment has been completed (24 hours should be sufficient), remove most of the active substance from the water by carrying out several large water changes.
A further treatment may be necessary after 2 weeks.
Levamisole is relatively harmless to invertebrates. In our aquarium, at least some of the apple snails and tower cover snails, along with a few shrimps, survived a bath treatment unscathed.
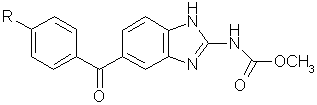
Mebendazole (R = -H)
IUPAC: Methyl-5-benzoyl-2-benzimidazole carbamate
Molecular formula: C16H13N3O3 (MG: 295.29)
Flubendazole (R = -F)
IUPAC: Methyl-5-(4-fluorobenzoyl)-2-benzimidazole carbamate
Molecular formula: C16H12FN3O3 (MG: 313.28)
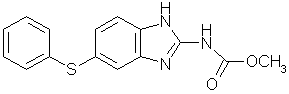
Fenbendazole
IUPAC: Methyl-5-(phenylthio)-2-benzimidazole carbamate
Molecular formula: C15H13N3O3S(MG: 299.35)
Effect and application
Benzimidazole carbamates prevent the worms from feeding. They slowly starve to death.
They reliably kill all snails and also pests such as planarians and hydra. Crayfish and shrimps often survive the treatment largely unharmed (no guarantee!).
After treatment, it can take weeks and sometimes months until the concentration of benzimidazole carbamates in the aquarium has fallen to such an extent that snails can be reintroduced.
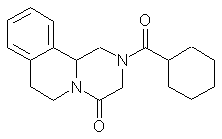
Praziquantel
IUPAC: 2-cyclohexylcarbonyl-1,6,7,11b- tetrahydro-2H-pyrazino[21-a]isoquinolin-4-one
Molecular formula: C19H24N2O2 (MG: 312.41)
Application
A feed treatment is usually successful. A mixture of 4 - 5 mg praziquantel per g of feed is fed for 3 days.
Bath treatment is only rarely necessary and can unfortunately also be associated with side effects.
For this purpose, 5 - 10 mg/l praziquantel is dissolved.
It is said that armoured catfish do not tolerate the drug well at all. At the first sign of discomfort, the animals must be transferred to fresh water.
Reversible infertility of the treated animals has been reported as a side effect.
Properties and effects
Works particularly well against cestodes (tapeworms). It is effective against all intestinal stages of these parasites. Praziquantel is rapidly absorbed via the surface of the parasite and evenly distributed throughout the parasite. It causes lasting damage to the outer skin with subsequent contraction and paralysis of the parasite.
Praziquantel is rapidly absorbed percutaneously and reaches maximum serum levels within 3 - 4 hours. Metabolisation takes place in the liver. Excretion takes place within 48 hours of application, mainly via the kidneys and to a lesser extent via the bile into the faeces.

