Carbon dioxide
The following information can be found, for example, in Klaus-D. Krinninger, Kohlendioxid - Kohlensäure - CO2

EXTRACTION
- Production
- Natural volcanic CO₂ sources
- Combustion of fossil fuels
- Hydrogen production in refineries
- etc.

Physics
With a density of 1.977 kg/m3 under standard conditions (1013 mbar, 0 °C), CO2 is around 1.5 times heavier than air and can therefore displace it when it escapes into deeper areas.
There is therefore a risk of suffocation from the colourless and odourless gas.

CHEMISTRY
CO2 is used in the beverage industry, but also to neutralise alkaline waste water.
As the resulting carbonates are strong buffers and the carbonic acid is only a weak acid, largely neutral waste water is produced without complex controls. Due to its non-toxicity and environmental friendliness, CO2 is therefore well suited for such tasks.
PHYSIOLOGY
Due to its high density, escaping carbon dioxide can displace the air, especially near the ground, and therefore reach concentrations that can lead to breathing difficulties and subsequently to unconsciousness and even death from suffocation.
This already occurs with a proportion of 7 - 10 % in the air.
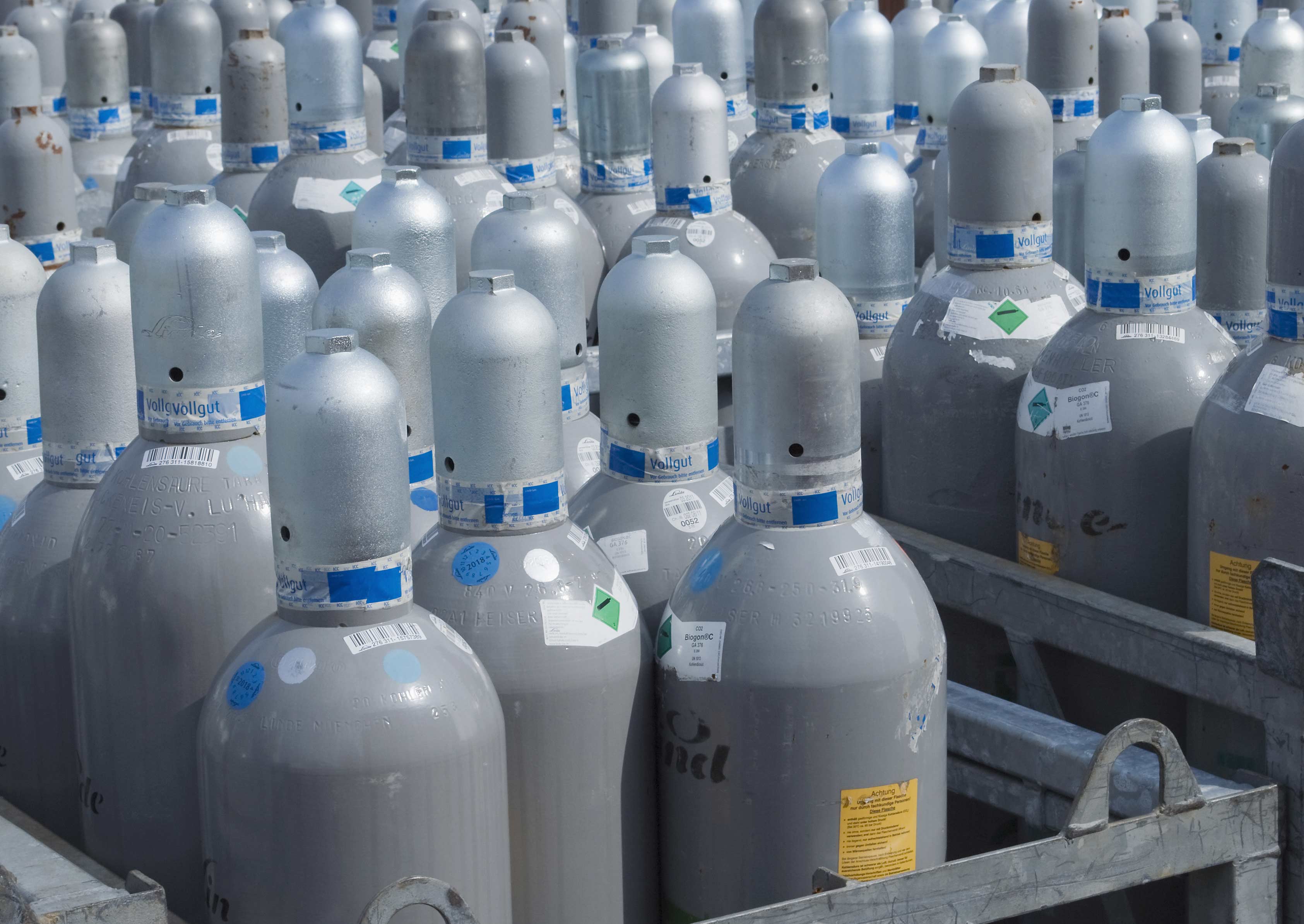

TRANSPORT
Only the transport form of the pressurised gas cylinder is interesting for aquaristics. Liquid CO2 and dry ice are probably unsuitable for aquaristic purposes and are also oversized.

ENVIRONMENT
CO2 in the air is one of the foundations of life on earth. The only problem is the rapid increase in this trace gas since the beginning of industrialisation.



